Decarbonizing buildings with geothermal energy heat pumps
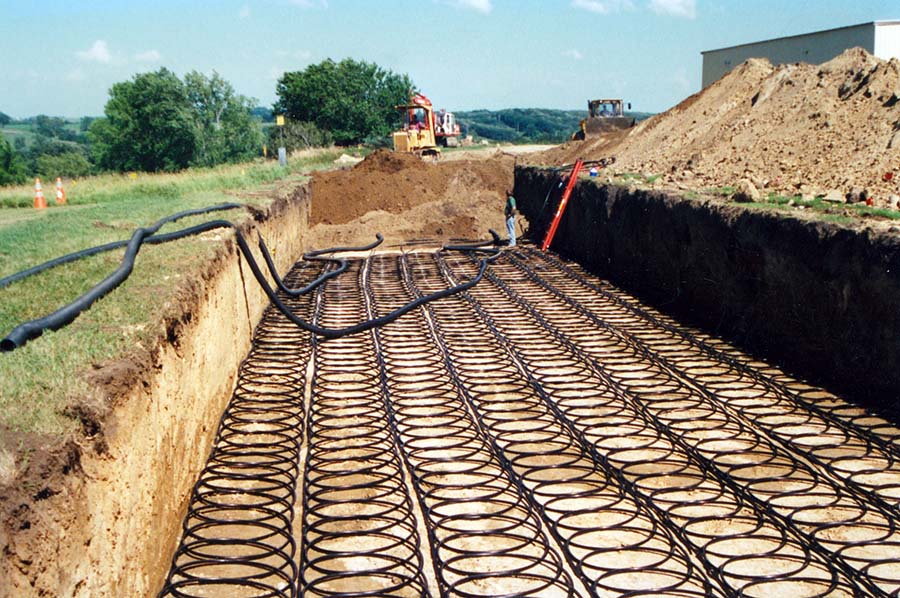

RENEW Energy Partners specializes in funding energy-saving retrofits for your commercial, industrial, and institutional buildings. We install many different technologies to make your buildings more efficient and reduce your energy bill. One strategy for significant savings is upgrading your HVAC systems to use geothermal energy.
What is geothermal energy?
Geothermal energy is a form of renewable energy that takes advantage of the temperature difference between the air outside and deep underground. Underground temperatures are more stable than above ground. This effect is exaggerated the deeper you go, with underground temperature stabilizing at about 10 degrees Celsius (50 degrees Fahrenheit) 30 feet under the ground all year. Moving heat from the ground in the winter and to the ground in the summer can dramatically reduce the energy required to meet a building’s heating and cooling needs year-round.
Significant progress has been made in over the last decade in reducing electricity use in buildings and installing renewable sources of electricity such as on-site solar, but the same has not been true of building heating and cooling systems which typically center on oil or natural gas fired boilers. RENEW Energy Partners can fund installation of geothermal heat pumps as an energy-saving retrofit and as a part of new construction, and thereby reduce reliance on fossil fuels on site, reduce energy costs, and reduce a building’s carbon footprint.
What are geothermal energy heat pumps?
Just as an air-source heat pump moves heat through the air from the inside to the outside in summer and from the outside to the inside in winter, a ground-source heat pump uses the heat from the Earth instead of the air. Because the temperature underground is a constant 50F, fluctuating much less than air temperatures, geothermal heat pumps can more efficiently heat and cool buildings than their air-source counterparts.
In colder climates, it is common to incorporate an electric heat source to provide supplementary or backup capacity. Heat pumps can be more environmentally friendly since they do not burn fossil fuels like oil or gas furnaces. Because these systems utilize that constant 50F heat from the earth they may also consume less energy than boilers or furnaces to provide the same heat, lowering a building’s energy cost.
Water Source Geothermal Heat Pumps (WSHP)
While ground-sourced heat pumps are what most people think of when they think of geothermal, water-source geothermal heat pumps are equally useful. They use bodies of water as a heat sink or source. This is often groundwater beneath the earth’s crust but can also be from a nearby body of water.
Types of Geothermal Heat Pump Systems:
Ground Loop Systems
Geothermal heating and cooling systems can be categorized into two types: open loop and closed loop. Open loop systems interact directly with the water source, whereas closed loop systems interface with the water source via a loop of coils of plastic tubing connecting in and out of the building. While closed loop systems tend to be the most common, the system choice depends on factors such as climate, soil conditions, available land, and installation costs. All buildings can utilize these systems, but they are especially cost effective when performing large retrofits for commercial, institutional, and industrial buildings.
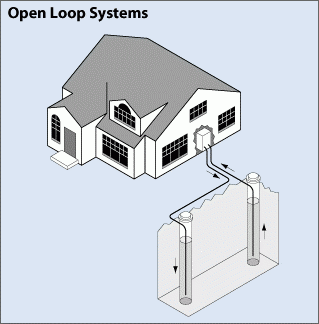
Open Loop Systems
Open loop systems in geothermal heat pump (GHP) systems use well or surface body water as the heat exchange fluid. The water circulates directly through the GHP system and then returns to the ground through a well, recharge well, or surface discharge.
Closed Loop Systems
Closed-loop geothermal heat pump systems, commonly used in geothermal heating and cooling, circulate an antifreeze solution through an internal plastic tubing circuit buried in the ground or submerged in water. The heat exchanger plays a vital role in transferring heat between the refrigerant in the heat pump and the antifreeze solution. Another type of closed-loop system called direct exchange, uses copper tubing buried in the ground without a heat exchanger. The three types of closed loop systems are horizontal, vertical, and pond/lake.
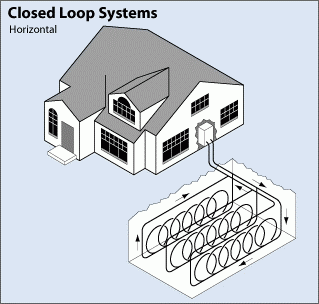
Horizontal Systems
The horizontal loop system is the most cost-effective installation for geothermal systems, particularly in residential settings. The most common layouts involve using two pipes buried at different depths or side-by-side in a trench. This requires a shallower dig but requires more land relative to its capacity.
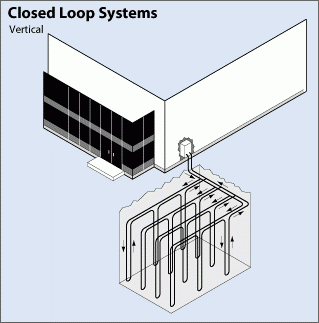
Vertical Systems
Large commercial buildings and schools often have land as a constraint. Vertical systems help bypass these limitations by using shallow soil while minimizing disruption to existing landscaping. Dig costs can be significantly higher than a horizontal system.
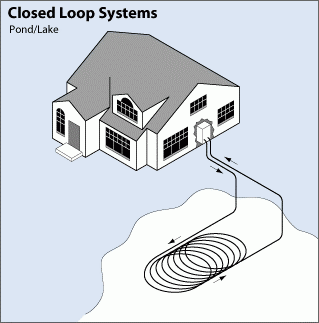
Pond/Lake Systems
These systems could be the most affordable option if a system has access to a body of water. A supply line pipe is run underground from the building to the water and coiled into circles at least eight feet under the surface to prevent freezing. The coils should only be placed in a water source that meets minimum volume, depth, and quality requirements.
Hybrid Systems
Hybrid systems combine different geothermal resources or a geothermal resource with outdoor air (such as a cooling tower). They are a viable technological option for meeting cooling needs greater than heating needs.
How can the use of Geothermal Heat Pumps reduce carbon emissions?
Geothermal heat pumps (GHPs) can significantly reduce carbon emissions by utilizing the Earth’s natural heat. Specifically:
High Efficiency
Efficiency is a major strength of geothermal systems. These systems transfer heat between the building and the ground, which requires less energy than traditional HVAC systems. This increased efficiency leads to reduced energy consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions. For more information on HVAC upgrades using heat pumps, see our blog post on the future of HVAC retrofits.
Renewable Energy Source
Geothermal heat pumps provide a renewable energy source for heating and cooling systems. Unlike fossil fuel-based systems, these pumps extract heat from the Earth’s core, continuously generating heat through natural processes. This ensures a consistent and sustainable energy supply for the heat pump.
Lower Electricity Demand
Since geothermal heat pumps require less energy to operate than conventional HVAC systems, they can help reduce the overall electricity demand of a building. Lower electricity consumption means fewer emissions from power plants, especially if the electricity is generated from fossil fuels.
No Combustion Emissions
Geothermal heat pumps do not burn any fuel to produce heat. Instead, they use electricity to facilitate heat transfer. This absence of combustion emissions eliminates the release of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other harmful pollutants associated with traditional heating systems, such as gas or oil furnaces.
Heat Recovery
Geothermal exchange systems can recover waste heat from cooling processes and utilize it for other purposes, such as water heating. This improves their energy efficiency and reduces their reliance on additional energy sources.
Long Lifespan
Geothermal heat pumps generally have a longer lifespan than traditional HVAC systems. Their underground components can last for decades in areas that aren’t tectonically active, reducing the need for frequent replacements and associated manufacturing emissions.
Grid Independence
In some cases, geothermal heat pumps can be used in off-grid or remote locations where connecting to a centralized power grid might be difficult or environmentally damaging. They can mitigate the environmental impact of extending power infrastructure to these areas by operating independently.
What are the financial benefits of using geothermal energy for building owners?
Reduced Energy Costs
Geothermal heat pumps are energy-efficient and can greatly reduce the energy used for heating and cooling. Building owners implementing this energy retrofit can expect to see savings in energy costs, with noticeable results within a few years. The exact amount of savings will vary depending on factors such as the size and location of the building, as well as energy prices. However, it is common for building owners to experience significant reductions in utility bills.
Enhanced Property Value
Retrofitting commercial buildings to implement geothermal energy heat pumps may increase property value and market appeal. Energy-efficient and sustainable features can attract potential buyers or tenants, creating a competitive advantage in the real estate market.
Access to Incentives and Tax Benefits
Many governments and local authorities offer incentives and tax benefits to encourage the adoption of renewable energy for building decarbonization, including geothermal. Building owners may be eligible for grants, tax credits, or other financial incentives to offset the initial installation costs and improve the financial viability of the geothermal energy project. For instance, the Department of Energy has announced $13 Million to support geothermal heating and cooling in communities.
Positive Public Image
Renewable energy technologies like geothermal can enhance a building owner’s reputation and brand image. Demonstrating a commitment to sustainability and environmentally responsible practices can resonate positively with customers, stakeholders, and the broader community.
No matter how you decide to implement energy efficiency measures in your building, these kinds of projects require funding. To fund an energy efficiency project for your building(s), RENEW Energy Partners offers an energy service agreement (ESA). The Energy Service Agreement:
- It may be treated as an off-balance sheet transaction. In that case, you do not own or carry the asset on your balance sheet (consult your tax advisor to evaluate your options).
- RENEW provides preventive and corrective maintenance in the service agreement.
- Your payment to RENEW will be based on the energy savings confirmed once the system is operational.
The RENEW Energy Service Agreement allows businesses to focus on what they do best while ensuring that their facilities are performing at their peak with brand-new and high-efficiency equipment. In this current climate of cost control and resource allocation, the energy service agreement is the perfect solution to help businesses meet sustainability goals and keep facilities in top condition. Reach out to RENEW and talk to us about financing your energy-saving retrofits today.
Sources: DOE




